Sex Linked Diseases

Sex Linked Diseases
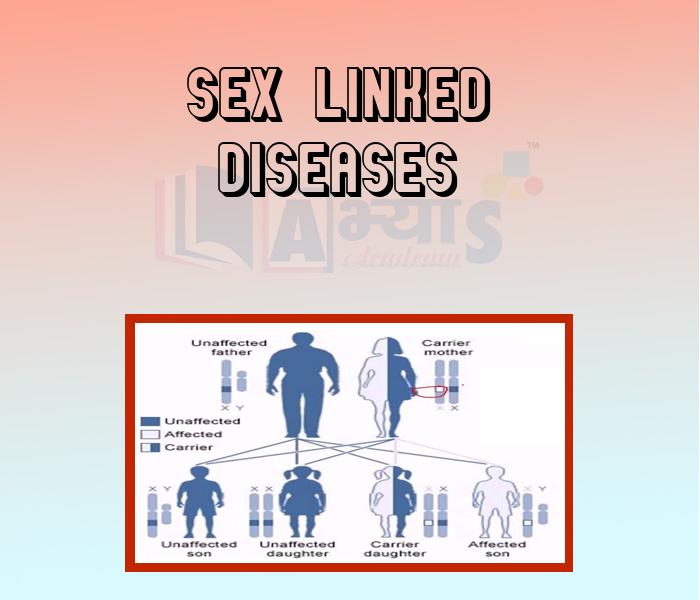
Sex linked is a trait in which a gene is located on a sex chromosome. In humans, the term generally refers to traits that are influenced by genes on the X chromosome. This is because the X chromosome is large and contains many more genes than the smaller Y chromosome. In a sex linked disease, it is usually males who are affected because they have a single copy of X chromosome that carries the mutation. In females, the effect of the mutation may be masked by the second healthy copy of the X chromosome.
'X' Linked inheritance :
Certain disorders caused due to heredity such as haemophilia and colour blindness are more common in males than in females. Such defects are due to recessive genes, which occur on the 'X' chromosome.
Haemophilia is a genetic disorder in which the sufferers are at a risk of bleeding to death because the blood fails to clot in them. Rare cases of haemophiliac males do occur but practically, none of haemophilic females.
The following cases explain the sex linked in humans.
Case I
Normal mother X Colour blind father
image reqiured
Case II
Carrier mother X Normal father

Case III
Colour blind mother X Normal father

Y linked inheritance
The Y chromosome linked traits occur in males but not in females. for eg :- traits such as hypertrichosis of ears and pattern baldness are found in men only.
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
It was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.
